Business opportunity
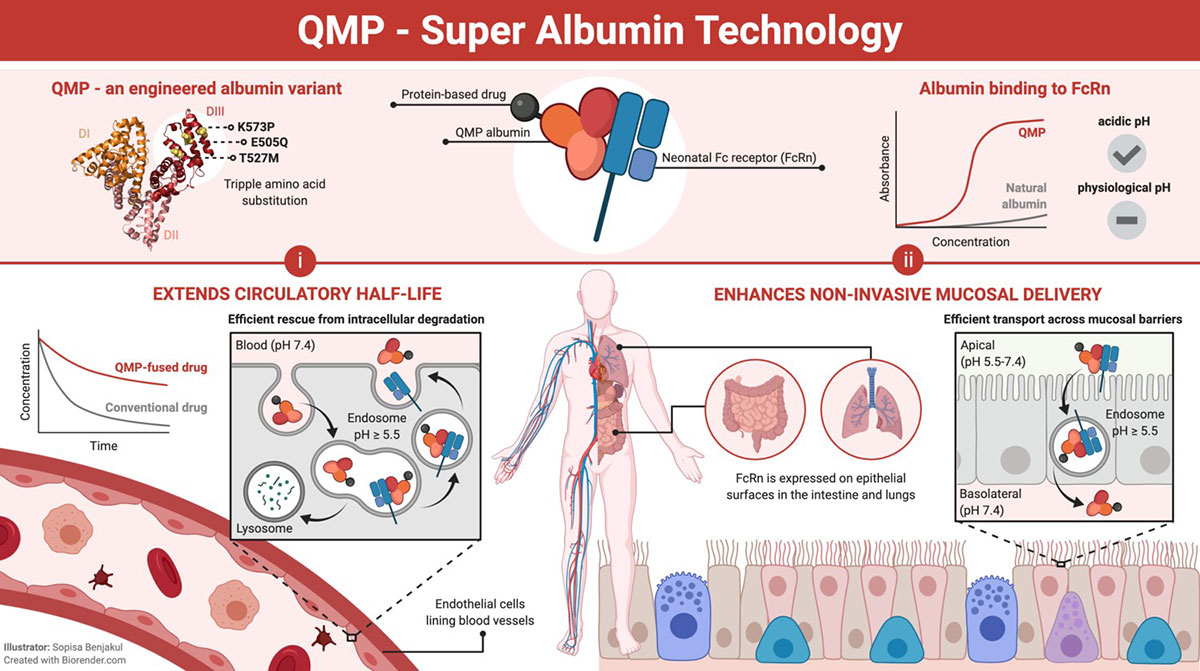
Inventors at the University of Oslo/Oslo University Hospital have developed an engineered human albumin variant with extended in vivo half-life. This unique albumin can be used as a fusion partner to improve the pharmacokinetics of molecules that otherwise would have short half-life. This will improve their therapeutic efficacy. In addition, the albumin variant has an increased transport capacity across polarized cellular layers when fused to therapeutic candidates.
Rapid clearance of biologics hampers the therapeutic efficacy of many promising peptide and protein based drug candidates. To maintain a sufficiently high working concentration, costly repeated doses at higher, potentially toxic, concentrations are required. Thus, there is a need for strategies to improve and tailor their pharmacokinetic properties. The albumin half-life extension technology may solve this major obstacle. In addition, the technology enhances delivery of fused biologics across mucosal barriers. As such, this may pave the way for needle-free delivery.
Technology
The optimized albumin was designed based on optimizing the affinity to the FcRn receptor.
Advantages
Albumin has a natural long half-life due to pH dependent binding to FcRn. The designed human albumin molecule has improved pH dependent FcRn binding kinetics that extends the half-life beyond that of natural albumin. This property can be utilized to improve the pharmacokinetics of drug candidates. The engineered albumin variant is also transported across polarized cellular layers more efficiently that natural albumin, and therefore may be utilized as a carrier for needle-free mucosal delivery.
Intellectual Property
Granted patents in US, EPO, JP, CA, KR, and CN (based on WO2015063611)
Publications
Super Albumin: https://stm.sciencemag.org/content/12/565/eabb0580
Super Albumin for improved hemophilia B treatment: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/bjh.17559 . Watch the video on this application here.